 |
 |
Bill Brodhead WPB Enterprises Inc
Radon & Vapor Intrusion |
 |
 |
|
Bill Brodhead WPB Enterprises Inc.
Radon & Vapor Intrusion |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
Radon Snifers can be Very Useful
We tested three available radon sniffers in 2021 that
cost less than 2000 dollars.
Here are the benefits and uses of a sniffer for a radon mitigator. 1) Quickly identify if a floor drain or utility pipe routed through a foundation is a radon source 2) Measure radon levels below a slab to determine if any slabs do or do not need an ASD system 3) On the spot measurements of radon level differences between rooms or crawl space or floors 4) Check if an adjacent slab positioned near the top of a basement foundation wall is a radon source 5) Measure radon levels inside a block wall 6) Determine if ventilation or system installation is reducing radon levels 7) Measure bathroom with shower running to qualify there is high radon in water 8) Measure radon fluxing through a concrete foundation or slab 9) Determine if sub-slab radon has a percentage of thoron Bill tested the RadonAway GM1-2, the Environmemtal Instruments Canada CT007-R and the Ecosense Ecotrackers. The Durridge RAD7 monitor also includes a sniffer mode and thoron mode but this instrument costs over $7000 and would typically not be a consideration for radon mitigators. In the past the Pylon AB5 was used as a sniffer but this model has been replaced by a larger unit that is similar in cost to th RAD7 and not practical for sniffing RadonAway GM1-2 price in 2021 - $1515
This is the RadonAway GM1-2. It includes a micro-monometer that was not a part of the evaluation. Data obtained from the GM1-2 cannot be saved, downloaded or display as a graph of the results. The pump moves about 0.4 lpm at a maximum suction pressure of 4.5 inches of vacuum. Other tested GM1-2's had higher airflow of about 0.8 lpm. The sniffer is supplied with a desiccant filled tube that changes from a blue to a pink color as it absorbs moisture in the sample. Extra desiccant needs to be purchased or the existing desiccant needs to be dried in an oven when it turns pink. After a one minute start up, the GM1-2 provides a radon result every six minutes as well as the previous average counts per minute it measured. During the six minute interval, the number of alpha counts happening are displayed. This allows recognizing a high radon level is being sampled. The previous six minute interval radon levels are displayed. No record is kept of earlier/previous readings. This requires the mitigator to be careful to record each interval separately so that a measurement interval is not forgotten or observed. The GM1-2 has radon sensitivity of 0.17 cpm/pCi/l exposure and a maximum measurement of 999 pCi/l The maximum radon level for the GM1-2 of 999 pCi/l is can commonly exceeded if sub-slab radon levels are measured. Once a radon level of a 1000 pCi/l or higher is sampled, making additional sniffer measurements in lower concentration areas is not possible for several hours. The GM1-2 tended to report the radon levels as about 70% to 80% of the chamber levels after one to two six minute intervals. When the sniffer was placed in a low radon area the GM1-2 reported about 10% to 25% of the original chamber sampled level in two intervals. Subsequent intervals in outdoor air continued to produce lower average measurements. IMPORTANT for Sniffer use For all sniffers it is important to minimize sampling time to reduce background counts and thus allow testing other locations. It is also very important because of accumulated background counts to always measure assumed lower radon areas before sampling assumed higher radon level areas.
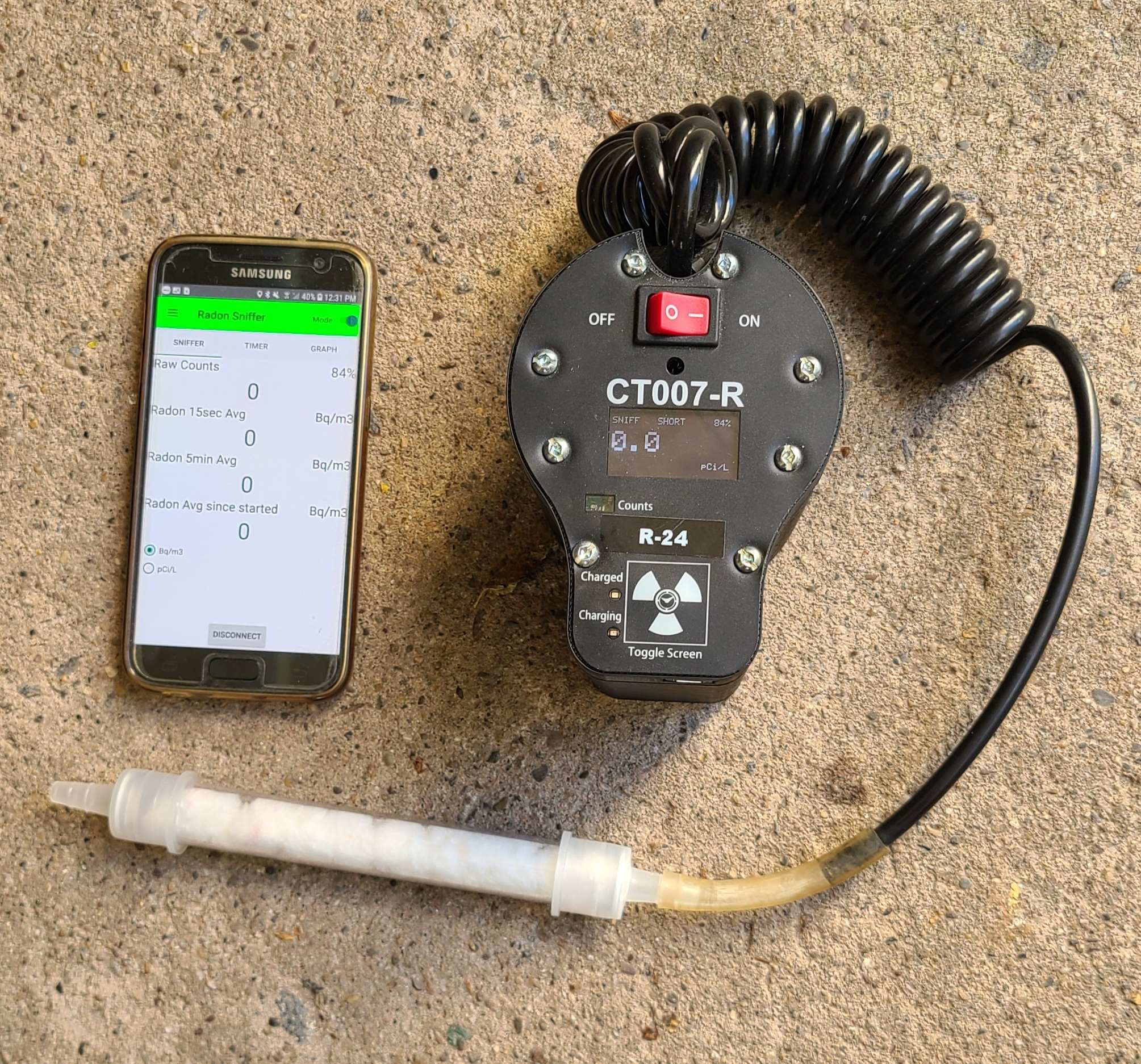
Environmental Instruments Canada CT007-R price in 2021 - $1750 This is the Environmental Instruments Canada CT007-R. By pressing the toggle switch, the display on the unit provides either the running 15 second average radon levels or the 5 minute running average. The battery charge level is also displayed. The data produced by the CT007-R is stored on cell phone via a Bluetooth connection and app software. The cell phone needs to remain in bluetooth range to continue receiving data. If the bluetooth goes out of range and then re-connects later it will pick up where it left off. The settings page of the app allows all the different parameters to be turned on or off or set to specific levels.
The pump moves about 0.6 lpm at a maximum suction pressure of 8.0 inches of vacuum. The CT007-R starts recording as soon as it is turned on. The app can be started before or after the CT007-R is turned on. The average intervals displayed are 15 seconds and 5 minutes. The unit can be set for longer data logging intervals if hourly measurements are desired to be recorded as data to be downloaded. As each alpha decay is detected it is displayed as a "Raw Count". The alpha counts recorded can also be audible beeps. This allows easy recognizing that a high radon level is being sampled.
In the cell phone app there are three standard tabs and an optional thoron tab. The 1st is the running averages plus alpha count display. The second tab is a timer for keeping track of any interval length defined. The third tab provides a graph of the running result. The interval of the graph can be varied from 15 second to 30 minutes by sliding a bar. This allows easily adjusting the graph to provide the best representation of the average radon levels that were measured. By moving tthe sniffer to different locations and keeping a written or memory of where the sniffer has been located and for how long one can see the radon variation in each new location sampled. In the graph displayed, CT007-R was exposed to 19 pCi/l twice and outdoor radon levels twice with about a 3 minute average set on the slider. The variation in individual results are significant but the the overall averages can be approximated. Note in this graph the final outdoor exposure is significantly higher than the 1st outdoor results which is likely due to increased background couints from the longer exposure to 19 pCi/l chamber. If sampling time is minimized then background counts fall to low levels more frequently. The CT007-R can measure radon levels as high as 25,000 pCi/l which makes it suitable for measuring sub-slab radon levels. The CT007-R has radon sensitivity of 0.78 cpm/pCi/l exposure. The CT007-R tended to report the radon levels as about 90% to 120% of the chamber levels after only a few minutes. When the sniffer was placed in a low radon area the CT007-R reported about 10% to 20% of the original chamber sampled level.
Sub-slab measurements typically contain some thoron which all the sniffers depict as radon levels. The percentage of thoron can be as much as 90% of the sub-slab measurement the sniffer identifies. The CT007-R has a thoron option that identifies the approximate level of sub-slab thoron versus sub-slab radon. It performs this function by a sequence that samples for 90 seconds. The pump then turns off for 300 seconds or six minutes. During this period the software anaylzes the fall off of alpha counts versus the ingrowth of radon counts. The change over time and the total count allows the algorithm to determine the levels of both radon and thoron as well as the percentage of each. If sub-slab measurements are being made in a slab it is important to disconnect the sniffer as soon as the 90 seconds of sample pumping is completed. Any sub-slab postive or negative presure will clear the CT007-R chamber while the pump is turned off and give a false reading.
Ecosense Ecotrackers price in 2021 - $999
The Ecotrackers do not have any air pumps. They are passive radon monitors with relatively high sensitivity at 0.50 cpm/pCi/l and an easy pathway to the ion chamber detector. This allows the monitors to have a fast response time to changing radon levels. The Ecotrackers have the same body and ion chamber design as the Radoneye RD200 and the Radoneye Pro. The Ecotrackers have a unique interface with the cell phone Ecotracker app.
The cellphone app connects to the Ecotracker by a bluetooth connection. Each individual Ecotracker can be setup to average the radon results every 5 minutes or every 10 minutes or every hour. The Ecotrackers measured between 60% and 70% of the three radon chamber radon levels after as little as five minutes. Leaving the Ecotrackers exposed for another five minutes is recommneded to confirm the 1st interval results. When the Ecotrackers were moved outdoors they measured between 10% and 14% of the chamber results.
The Ecotrackers have a maximum measurement level of 255 pCi/l. The monitors begin recording after a three minute warm up. Each interval they store the data and then display the previous measurement on the top of the monitor and on the app device page. If multiple Ecotrackers are within blue tooth range all the Ecotrackers current radon results will be displayed.
If an individual Ecotracker is opened in the app, a graph can be displayed of all the interval results. The results can also be saved as a text file and uploaded to a cloud or emailed to anyone. The text file can be brought into a spreadsheet for graphing or review. The Ecotrackers cannot be used to measure inside block walls or below a slab because they have no pump and have a maximum measurement level of 255 pCi/l. They need to be placed near a suspected radon source like a floor drain or an open utility pipe or inside a crawl space. Because the package includes four monitors they can be placed in different areas of the foundation or slab to try and determine a radon source based on the variation in radon levels from one location to another. Radon diffuses rapidly in an open room or area. In general you need to place monitors carefully to maximize their ability to locate a radon source.
Finding a Tricky Source with a Sniffer
To assist the location of this source it would be helpful if additional negative pressure could be generated in the basement to try and induce a flow out of the source. Sometimes small clues like discolored fiberglass or spider webs indicates an airflow exists. Other times it may be necessary to leave the Ecotrackers in place for 24 hours after re-setting the interval to hourly in order to see differences between Ecotrackers of just a few pCi/l with night time often providing a stronger negative pressure in the basement.
If it is suspected that radon levels may be coming directly through or out of the concrete slab the CT007-R can be used to measure the radon levels under the concrete slab. The thoron contribution to the sub-slab radon levels should also be also measured with the CT007-R Ecotrackers can be used to measure the actual emanation coming through the slab. It is unlikely that there would be any thoron coming through the slab because of the diffusion time delay. The Ecotracker is placed under a 3 liter metal mixing bowl with gasket sealer attached to the edge. The Ecotracker and battery are connected and placed under the bowl for about 12 to 24 hours with a weight on the bowl to compress the gasket. The increase in radon over several hours is divided by the hours of the increase. This amount is multiplied by 2.5 which is the bowl size minus the volume of the Ecotracker and the battery and cord. This result is divided by the area of the bowl which for a standard 3 liter bowl is about 0.3276 ft2. Conclusions Each of these sniffers would be valuable for the radon mitigator especially when they have a radon system installation that appears to be working as planned but it is not reducing the radon levels below the guideline or original contract mitigation level. The first plan of action with elevated post mitigation results and a common active soil depressuriztion ASD system is installed is to carefully determine if the system is depressurizing under the entire soil contact slab. If there is inadequate or no sub-slab negative pressure under parts of the slab then this needs to be addressed first. Sniffers can be used at cracks and slab openings where there is positive pressure under a slab to confirm lack of pressure is the issue. Once it is determined that the sub-slab has negative pressure then it typically means there is an untreated source. The sniffer is your one tool to try and determine where this untreated source can be. Here is a list of possible untreated other sources.
Untreated crawl space - Untreated other slab - Floor
drain open to non-depressurized soil - Good luck finding that invisible radon entry source.
|
 |
|
Download
Use of Radon Mitigation Sniffers paper
Use of Radon
Sniffer slides
|
 |
 |
Radon Snifers
|
|
Download:
|
|
|
 |




 One
problematic location in basement style homes is when a concrete slab
butts up to the outside of the basement foundation near or above the
wood framing sill plate. A common example of this is a garage or
front entrance slab that is only one step down from the first floor
flooring. Radon becomes trapped under these slabs and moves
sideways under or through the sill plate and box framing because the
basement is negative in pressure compared to the sub-slab under these
adjoining slabs. By either placing an Ecotracker at the most
suspect location or holding the inlet tubing of the GM1-2 or the CT007-R
it is hoped the radon entry point can be discovered.
One
problematic location in basement style homes is when a concrete slab
butts up to the outside of the basement foundation near or above the
wood framing sill plate. A common example of this is a garage or
front entrance slab that is only one step down from the first floor
flooring. Radon becomes trapped under these slabs and moves
sideways under or through the sill plate and box framing because the
basement is negative in pressure compared to the sub-slab under these
adjoining slabs. By either placing an Ecotracker at the most
suspect location or holding the inlet tubing of the GM1-2 or the CT007-R
it is hoped the radon entry point can be discovered.